REMOTE SENSING
Remote sensing is the science of obtaining of an
object or areas in the earth surface and in atmosphere and oceans by means of
propagation of signals.
Remote sensing allows the communication with the
satellites with other medium and transmits signals in a wide area without make
physical contact with the object such as its wireless. The information can be
accessed after being propagated (electromagnetic radiations).
Remote sensors collect data in the form of images and provide specialized capabilities for manipulating, analyzing, and visualizing those images.
Remote sensors can be categorized into two parts
·
Passive Sensors
·
Active Sensors
PASSIVE SENSORS
Passive sensors are responsible to respond for external stimuli and record
radiation that is reflected from earth’s surface. These are usually comes from
sun and used to collect data during daylight hours.Therefore passive sensors produce the natural radiation and that is emitted or reflected by the objects to the surrounding areas. Examples of passive sensors it include Radiometers, Infrared, photography and change-coupled device.
ACTIVE SENSORS
Active sensors are responsible to respond internal stimuli in collecting a
data about the earth and it emits energy in order to scan objects and areas
that sensor detects and measure radiation that reflected backscattered from the
targetExample a laser-beam remote sensing system projects a laser onto the surface of Earth and measures the time that it takes for the laser to reflect back to its sensor.
Active remote sensing, in contrast, depends on an artificial
"light" source, such as radar, to illuminate the scene.
Remote sensing depends upon
measuring some kind of energy that is emitted, transmitted, or reflected from
an object in order to determine certain physical properties of the object.
Remote sensing also replaces costly and slow data collection on the ground,
ensuring in the process that areas or objects are not disturbed.
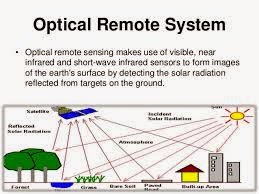
OPTICAL REMOTE SENSOR
Optical remote sensor has an ability of detecting solar radiation reflected
or scattered from the earth, forming images resembling photographs taken by
camera high up in space. The wavelength region usually extended from visible
and near infraredOptical remote sensing involves acquisition and analysis of optical data – electromagnetic radiation captured by the sensing modality after reflecting off an area of interest on ground. Optical image acquisition modalities have come a long way – from gray-scale photogrammetric images to hyper spectral images.
ENERGY STRIKES IN THE EARTH SURFACE
Radiation that is not absorbed or scattered in the atmosphere can reach and
interact with the Earth's surface. There are three forms of interaction that
can take place when energy strikes, or is incident upon the surface. These are absorption, transmission, and reflection. The total incident energy will interact with the surface in one or more of these three ways. The proportions of each will depend on the wavelength of the energy and the material and condition of the features.
VEGETATION
Remote sensor play the great role on the growth of the vegetable where by chlorophyll
strongly absorbs radiation in the red and blue wavelengths but reflects green
wavelengths. Leaves appear "greenest" to us in the summer there is
less absorption and proportionately more reflection of the red wavelengths, making
the leaves appear red or blue.The wavelength of the sunlight penetrates to the chlorophyll and synthesis their own food and accumulate the large group of the people in utilize the energy resource. In such this can balance the ecosystem.
REMOTE SENSING IMAGES AND MAPS
Maps are particularly helpful in interpreting remote sensing data. Topographic maps are foremost among maps which help clarify many terrain recognition ambiguities found on remote sensing images.Geological maps bring attention to formations conducive to particular types of hazards. This knowledge can assist in localization and the systematic search for these hazards.
Soils maps can serve a similar purpose, but to a lesser extent. Finally, vegetation and land-use maps can provide information on the moisture content, underlying geologic formations, and types of soils present.
Remote sensing has many uses in
disaster management, from risk modeling and vulnerability analysis, to early
warning, to damage assessment





No comments:
Post a Comment