SOLAR ENERGY
Solar energy is the energy from the
sunSolar energy is radiant light and heat from the sun harnessed using a range of ever-evolving technologies such as solar heating, solar photovoltaic, solar thermal energy, solar architecture and artificial photosynthesis.
Solar energy play a great role in the development in economic, socially and politics activities, Solar energy is the renewable source of energy that converted to solar power. The radiation of the sun can be captured with the solar panel and converted to solar power
The total solar energy absorbed by
Earth's atmosphere, oceans and land masses is approximately 3,850,000 exajoules
(EJ) per year. The amount of solar energy reaching the surface of the planet is
so vast that in one year it is about twice as much as will ever be obtained
from all of the Earth's non-renewable resources of coal, oil, natural gas, and
mined uranium combined
Solar energy can be harnessed at
different levels around the world, mostly depending on distance from the
equator.
Picha
Application
of solar technology
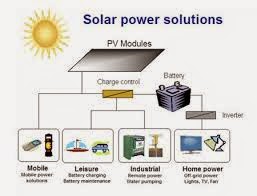
Electricity production
Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity,
either directly using photovoltaic (PV), or indirectly using concentrated solar
power (CSP). CSP systems use lenses or mirrors and tracking systems to focus a
large area of sunlight into a small beam. PV converts light into electric
current using the photoelectric
effect.
The electricity production leads to produce the
power that will process industries and home activities and give the significant
of growth of world.
Solar technologies are broadly characterized as either passive or active
depending on the way they capture, convert and distribute sunlight. Active solar techniques use photovoltaic panels, pumps, and fans to convert sunlight into useful outputs. Active solar technologies increase the supply of energy and are considered supply side technologies
Passive solar techniques include selecting materials with favorable thermal properties, designing spaces that naturally circulate air, and referencing the position of a building to the Sun.
Passive solar technologies reduce the need for alternate resources and are generally considered demand side technologies.
Cooking
Solar cookers use sunlight for cooking, drying and pasteurization. They can be grouped into three broad categories: box cookers, panel cookers and reflector cookers.
Solar cookers improve the recycled a source of energy and reduce the rate of emission of pollutant air basic box cooker consists of an insulated container with a transparent lid.
Panel cookers use a reflective panel to direct sunlight onto an insulated container and reach temperatures comparable to box cookers. Reflector cookers use various concentrating geometries (dish, trough, Fresnel mirrors) to focus light on a cooking container. These cookers reach temperatures of 315 °C (599 °F) and above but require direct light to function properly and must be repositioned to track the Sun.
Agriculture
Agriculture and horticulture seek to optimize the capture of solar energy in order to optimize the productivity of plants. Techniques such as timed planting cycles, tailored row orientation, staggered heights between rows and the mixing of plant varieties can improve crop yields.
Greenhouses convert solar light to heat, enabling year-round production and the growth (in enclosed environments) of specialty crops and other plants not naturally suited to the local climate. Greenhouses remain an important part of horticulture today, and plastic transparent materials have also been used to similar effect in polytunnels and row covers.
Transport
Some vehicles use solar panels for auxiliary power, such as for air conditioning, to keep the interior cool, thus reducing fuel consumption.
In 1975, the first practical solar
boat was constructed in England where at 1995, passenger boats incorporating PV
panels began appearing and are now used extensively. In 1996, Kenichi Horie made
the first solar powered crossing of the Pacific Ocean, and the sun21
catamaran made the first solar powered crossing of the Atlantic Ocean in the winter
of 2006–2007. There were plans to circumnavigate the globe in 2010.
A solar balloon is a black
balloon that is filled with ordinary air. As sunlight shines on the balloon,
the air inside is heated and expands causing an upward buoyancy force,
much like an artificially heated hot air balloon.
Some solar balloons are large enough
for human flight, but usage is generally limited to the toy market as the
surface-area to payload-weight ratio is relatively high.
Fuel Production
Solar chemical processes use solar energy to drive chemical reactions. These
processes offset energy that would otherwise come from a fossil fuel source and
can also convert solar energy into storable and transportable fuels. Solar induced chemical reactions can be divided into thermochemical or photochemical. A variety of fuels can be produced by artificial photosynthesis.
The multielectron catalytic chemistry involved in making carbon-based fuels (such as methanol) from reduction of carbon dioxide is challenging; a feasible alternative is hydrogen production from protons, though use of water as the source of electrons (as plants do) requires mastering the multielectron oxidation of two water molecules to molecular oxygen.
Hydrogen production technologies had been a significant area of solar chemical research since the 1970s. Aside from electrolysis driven by photovoltaic or photochemical cells, several thermochemical processes have also been explored.
One such route uses concentrators to split water into oxygen and hydrogen at high temperatures (2,300–2,600 °C or 4,200–4,700 °F). Another approach uses the heat from solar concentrators to drive the steam reformation of natural gas thereby increasing the overall hydrogen yield compared to conventional reforming methods.
Water heating
Solar hot water systems use sunlight to heat water. In low geographical
latitudes (below 40 degrees) from 60 to 70% of the domestic hot water use
with temperatures up to 60 °C can be provided by solar heating systems.The most common types of solar water heaters are evacuated tube collectors (44%) and glazed flat plate collectors (34%) generally used for domestic hot water; and unglazed plastic collectors (21%) used mainly to heat swimming pools.








No comments:
Post a Comment